|
Phần 2: Tổng hợp các nghiên cứu về chẩn đoán hình ảnh trên bệnh nhân sán lá gan lớn trên thế giới và Việt Nam
1.Keiser J, Shu-Hua X, Tanner M, Utzinger J et al., (2006). Artesunate and artemether are effective fasciolicides in the rat model and in vitro. J Antimicrob Chemother 57: 1139-1145. 2.Keiser J, Shu-Hua X, Jian X, Zhen-San C et al., (2006). Effect of artesunate and artemether against Clonorchis sinensis and Opisthorchis viverrini in rodent models. Int J Antimicrob Agents 28:370-373. 3.Keiser J, Utzinger J. et al., (2007). Advances in the discovery and development of novel trematocidal drugs. Expert opiniondrug discovery, 2(1):9-23 4.Keiser J, Utzinger J, J. Vennerstrom, Y. Dong et al., (2008). Activity of artemether and OZ78 against triclabendazole-resistant Fasciola hepatica. Transactions of the Royal Society of Tropical Medicine and Hygiene, vol.101, Issue 12:1219-1222. 5.Keyhan Ashrafi, Farshid Saadat, Sandra O’neill et al., (2015). The Endemicity of human fascioliasis in Guilan province, Northern Iran: The baseline for implementation of control strategies. Iran J Public Health, vol. 44, No.4:501-511. 6.Koc Z., Ulusan S., Tokmak N. et al., (2009). Hepatobiliary fascioliasis: Imaging characteristics with a new finding. Diagn Interv Radiol, (15):247-251. 7.Kuchai JA, Chishti MZ, Zaki MM et al., (2011). Some epidemiological aspects of fascioliasis among cattle of Ladakh. Global Vet;7: 342-346. 8.Lawrence M. Terney, Stephen J. Mcphee et al., (2005). Fascioliasis: Current medical diagnosis and treament. Lannge publising house, pp.1457-1465. 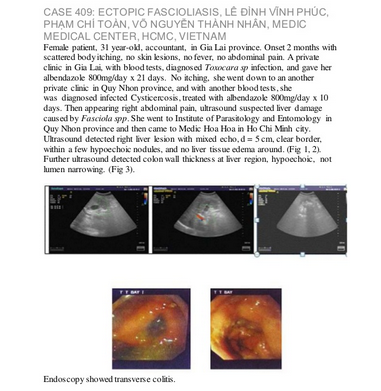
Hình 1
9.Magalhães KG, Jannotti-Passos LK, Caldeira RL et al., (2008). Isolation and detection of Fasciola hepatica DNA in Lymnaea viatrix from formalin-fixed and paraffin-embedded tissues through multiplex-PCR. Vet Parasitol;152:333-338. 10.Mage C, Bourgne H, Toullieu JM, Rondelaud D et al., (2002). Fasciola hepatica and Paramphistomum daubneyi: changes in prevalences of natural infections in cattle and in Lymnaea truncatula from central France over the past 12 years. Vet Res 2002;33: 439-447. 11.Mahami-Oskouei M, Dalimi A., Forouzandeh-Moghadam M et al., (2011). Molecular identification and differentiation of Fasciola isolates using PCR-RFLP method based son internal transcribed spacer (ITS1, 5.8S rDNA, ITS2). Iranian Journal of Parasitology, 5(3):35-42. 12.Marcilla JR, Bargues MD, Mas-Coma S et al., (2002). A PCR-RFLP assay for the detection of human infection between Fasciola hepatica and Fasciola gigantica. Molecular and Cellular Probes, 16(5):327-333. 13.Marcos L, Vicente Maco, Angélica Terashima et al., (2005). Fascioliasis in relatives of patients with Fasciola hepatica infection in Peru. Journal of Egyptian Society of Parasitology, 32 (1):317-354. 14.Marcos L. A, Terashima A. et al., (2007). Review-update on human fascioliasis in Peru: Diagnosis, treatment and clinical classification proposal. Neotrop. Helminthol, 1(2):85-103. 15.Marcos L. A., Terashima A., Gottuzzo E. et al., (2008). Update on hepatobiliary flukes: fascioliasis, opisthorchiasis and clonochiasis. Current opinion in Infectious diseases, (21):523-530. 
Hình 2
16.Marcos L. A., Tagle M., Terashima A. et al., (2008). Natural history, clinico- radiologic correlates and response to triclabendazole in acute massive fascioliasis. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg., (78):222-227. 17.Mas-Coma S, Bargues MD, Esteban JG et al., (1999). Human fasciolosis. Human fasciolosis. Wallingford, United Kingdom: CAB International Publishing, 411-434. 18.Mas-Coma MS, Esteban JG, Bargues MD et al., (1999). Epidemiology of human fascioliasis: a review and proposed new classification. Bull World Health Organ 77: 340-346. 19.Mas-Coma S, Funatsu IR, Bargues MD et al., (2001).Fasciola hepatica and lymnaeid snails occurring at very high altitude in South America. Parasitology, 123 Supplement:115-127. 20.Mas-Coma S, Bargues MD et al., (2004).Human fascioliasis: Epidemiological patterns in human endemic areas of South America, Africa, and Asia.Southeast Asian Jtrop Med Public Health, 35(1):1-11. 21.Mas-Coma S et al., (2005).Epidemiology of fascioliasis in human endemic areas. Journal of helminthology, 79 (3):207-216. 22.Mas-Coma MS, Bargues MD et al. (2005). Fascioliasis and other plant-borne trematode zoonoses. International Journal of Parasitology, 35(11-12):1255-1278. 23.Mas-Coma MS et al., (2007). Report human fascioliasis in Vietnam. Expedition of parasitology team of the Valencia university. 2007. 
Hình 3
24.Mas-Coma MS, Valero MA, Bargues MD et al., (2009). Fasciola, lymnaeids and human fascioliasis with a global overview own diseases transmission, epidemiology, evolutionary genetics, molecular epidemiology and control. Adv Parasit., 69:141-146. 25.S. Mas-Coma, M.D. Bargues, M.A. Valero et al., (2014). Diagnosis of human fascioliasis by stool and blood techniques: Update for the present global scenario. Parasitology, vol.141, Special issue 14:1918-1946. 26.Massoud A., El Sisi S., Salama O., Massoud Afaf. et al., (2001). Premilinary study of therapeutic efficacy of a new fasciolicidal drug derived from Commiphora molmol (Myrrh). Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 65(2):96-99. 27.McConville, M., Brennan, G.P., McCoy et al., (2006). Adult triclabendazole-resistant Fasciola hepatica: Surface and subsurface tegumental responses to in vitro treatmentwith the sulphoxide metabolite of the experimental fasciolicide compound alpha. Parasitology 133:195-208. 28.McGarry J W, Ortiz PL, Hodgkinsnon JE et al., (2007). PCR-based differentiation of Fasciola species (Trematoda: Fasciolidae), using primers based on RAPD-derived sequences. Annals of Tropical medicine and parasitology, 101(5):415-421. 
Hình 4
29.McKinstry B, Halferty, G.P. Brennan, I. Fairweather et al., (2009). Morphological response of triclabendazole-susceptible and triclabendazole-resistant isolates of Fasciola hepatica to treatment in vitro with nitroxynil (Trodax). Parasitology Research, vol.104(3):645-655. 30.McManus DP, Dalton JP et al., (2006). Vaccines against the zoonotic trematodes Schistosoma japonicum, Fasciola hepatica, Fasciola gigantica. Parasitology, 133:43-61. 31.Mel Figtree, Miles H Beaman, Rogan Lee et al., (2015). Fascioliasis in Australian travellers to Bali. Med J Aust;203(4):186-8. 32.Miguel M Cabada, Martha Lopez, Maria Cruz et al., (2016). Treatment failure after multiple courses of triclabendazole among patients with fascioliasis in Cusco, Peru: A case series. PLoS Negl Trop Dis 25;10(1):e0004361. 33.Millan JC, Mull R, Freise S, Richter J et al., (2000). The efficacy and tolerability of triclabendazole in Cuban patients with latent and chronic Fasciola hepatica infection. Am J Trop Med Hyg 63: 264-9. 34.Mojgan Aryaeipour, Eshrat Beigom Kia, Zahra Heidari, et al., (2015). Serological study of human fasciolosis in patients referring to the school of public health, Tehran university of medical sciences, Tehran, Iran during 2008-2014. Iran J Parasitol 2015;10(4):517-22. 35.Moghadami M., Mardani M. et al., (2008). Fasciola hepatica: A cause of obstructive jaundice in an elderly man from Iran. The Saudi Journal of Gastroenterology, 14(4):208-210. 36.Mojgan Aryaeipour, Soheila Rouhani, Mojgan Bandehpour (2014). Genotyping and phylogenetic analysis of Fasciola sp. isolated from sheep and cattle using PCR-RFLP in Ardabil province, Northwestern Iran. Iranian J Publ Health, Vol. 43, No.10: 1364-1371. 37.Moll L, Gaasenbeek CP, Vellema P et al., (2000). Resistance of Fasciola hepatica against triclabendazole in cattle and sheep in the Netherlands. Vet Parasitol 91:153-158. 38.Mottier L, Alvarez L, Fairweather I, Lanusse C et al., (2006). Resistance- induced changes in triclabendazole transport in Fasciola hepatica: Ivermectin reversal effect. J Parasitol 92:1355-1360. 39.Mramba Nyindo, Abdul-Hamid Lukambagire (2015). Fascioliasis: An ongoing zoonotic trematode infection. Biomed Res Int 2015 31;2015:786195. 40.Nabil AM Salmo, Snur MA Hassan, Azad K Saeed (2014). Histopathological study of chronic livers Fascioliasis of cattle in Sulaimani abattoir. AL-Qadisiya Journal of Vet. Med. Sci. Vol. 13 No. 2 2014. 41.Nayana U Patel, Tami J Bang, Gerald D Dodd (2016). CT findings of human Fasciola hepatica infection: case reports and review of the literature. Clin Imaging 2016;40(2):251-5. 42.Neil Mackintosh, Peter Brophy (2012). Measuring triclabendazole resistance as part of a whole farm strategy for the control of liver fluke in sheep and cattle. Final report, Institute of Biological, Environmental and Rural sciences (IBERS), Wales. 43.Overend DJ, Bowen FL et al., (1995). Resistance of Fasciola hepatica to triclabendazole. Aust Vet J 72: 275-276. Hình 5+6 44.Park S., Sohn S. et al., (2010). Cerebal ischemia caused by hepatic fascioliasis.Korean J Stroke, (12), pp. 33-35. 45.Parkinson M., O’Neill S.M., Dalton J.P. et al., (2007). Endemic human fascioliasis in the Bolivian Altiplano. Epidemiol infect, 135(4):669-674. 46.Patil K., Kulkarni S., Gorad K. et al., (2009), Acute fascioliasis - rare cause of obstructive jaundice: A case report. Bombay Hospital Journal, 51(3):398-400. 47.Huynh Hong Quang, Trieu Nguyen Trung et al., (2010). The human parasitic diseases and zoonosis in Central and West-highland of Vietnam (2005-2010): Situations and on-going projects/ studies at many levels. International seminar of Researchable Issues in Ecosystem Approaches to Health Management of Emerging Infectious Diseases in Southeast Asia in Bali, Indonesia, October, 2010. 48.Huynh Hong Quang, Nguyen Van Chuong et al., (2013), Some clinical manifestations and laboratory findings of human gigantica fascioliasis in pregnant women and children in Central coastal provinces, Vietnam 2003-2013. Journal for malaria and parasitic disease control, vol. 5-2013, ISSN 0868-3735, pp.21-31 49.Ratana Rujirakul, Naporn Ueng-arporn, Soraya J Kaewpitoon (2015). Risk areas of liver flukes in Surin province of Thailand using geographic information system (GIS). J Med Assoc Thai;98 Suppl 4:S22-6. 50.Rashed AMR A., Khalil H.H.M., Morsy A.T.A. (2008). Zoonotic ectopic fascioliasis: Review and discussion. J. Egypt. Soc. Parasitol, 38(1):591-608. 51.Reza Shafiei, Bahador Sarkari, Seyed Mahmoud Sadjjadi (2015). Performance of a 27 kDa Fasciola hepatica antigen in the diagnosis of human fascioliasis. J Lab Physicians.;7(1):17-20.17 52.Richter J, Freise S, Mull R, Millan JC, (1999). Fascioliasis: Sonographic abnormalities of the biliary tract and evolution after treatment with triclabendazole. Trop Med Int Health 4:774-781. 53.Roberts JA, Copeman DB (2006). Distribution of metacercariae of Fasciola gigantica on rice straw. Trop Anim Health Prod; 38:117-119. 54.Robinson, M.W., Lawson, J., Trudgett, A., Hoeyet al., (004). The comparative metabolism of triclabendazole sulphoxide by triclabendazole-susceptible and triclabendazole-resistant Fasciola hepatica. Parasitol. Res. 92, 205-10. 55.Saba R., Korkmanz M., Inan D., Mamikoglu L., et al., (2004). Human fascioliasis. Clinical Microbiology and Infection, 10(5):385-387. 56.M.A. Sabry E.S. Taher, N. Farag Allah et al., (2014). Diagnosis of Fasciola infection by SDS-PAGE eluted excretory secretory protein fractions using dot-ELISA. International Journal of Veterinary Science and Medicine 2:130-135 57.L. Savioli, L.Chitsulo, A.Montresor (1999). New opportunities for the control of fascioliasis. Bulletin of the World Health Organization, 77(4) 58.Shah S.A.A., Khan M.Y., Ahmad J. et al., (2010). Fascioliasis: A case of obstructive jaundice report, JPMI, 24(4):332-32. 59.Shalaby IM, Hassan MG, Soliman MFM et al., (2004). Factors affecting dynamics of metacercarial productivity of Fasciola gigantica from its snail host. Pakistan. J Biol Sci 2004;7: 393-398 
Hình 7

Hình 8
60.Sharifiyazdi H, Moazeni M, Rabbani F (2012). Molecular characterization of human Fasciola samples in Gilan province, Northern Iran on the basis of DNA sequences of ribosomal and mitochondrial DNA genes. Comp Clin Path 2012;21: 889-894. 61.Salazar L, Estrada VE, Velásquez LE (2006). Effect of the exposure to Fasciola hepatica (Trematoda: Digenea) on life history traits of Lymnaea cousini and Lymnaea columella (Gastropoda: Lymnaeidae). Exp Parasitol;114: 77-83. 62.Shu FF, Lv RQ, Zhang YF, Duan G, Wu DY et al., (2012). Characterization of Fasciola samples by ITS of rDNA sequences revealed the existence of Fasciola hepatica and Fasciola gigantica in Yunnan province. J Parasitol.;98(4):889-90. 63.Sobhon P, Anantavara S, Dangprasert T et al., (1998). Fasciola gigantica: studies of the tegument as a basis for the developments of immunodiagnosis and vaccine. Southeast Asian J Trop Med Public Health; 29:387-400. 64.Soo Young Choi, Jae Woon Kim, Jae Cheon Jang (2015). Hepatobiliary fascioliasis with multiple aneurysms and active bleeding: A case report.J Korean Soc Radiol 2015;72(4):291-294. pISSN 1738-2637 / eISSN 2288-2928 65.Sukhapesna V, Tantasuwan D, Sarataphan N et al., (1994). Economic impact of fascioliasis in buffalo production. J Med Assoc Thai 1994; 45:45-52. 66.Syed Ali Ahasan, M Adela Valero, Santiago Mas-Coma et al., (2016). CIAS detection of Fasciola hepatica/ F. gigantica intermediate forms in bovines from Bangladesh. Acta Parasitol 2016 Jun;61(2):267-77. 67.Taheri M.S., Aminzade Z., Shokohi S. et al., (2007). Hepatobiliary fascioliasis: Clinical and radiological features. Iranian J Parasitol, 2(4):48-55. 68.Talaie H, Emami H, Yadegarinia D, Nava-Ocampo AA et al., (2004). Randomized trial of a single, double and triple dose of 10 mg/kg of a human formulation of triclabendazole in patients with fascioliasis. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol 31:777-782. 69.Thomas AP et al., (1883). The life history of the liver-fluke (Fasciola hepatica). Quart J Microscop Sci;2: 99-133. 70.Thomas Fürst, Jennifer Keiser, Jürg Utzinger (2012).,Global burden of human foodborne trematodiasis: a systematic review and meta-analysis. The Lancet Infectious Diseases, Vol.12, Issue 3: 210-221. 71.Ubeira F.M., Muino L., Valero M.A., Periago M.V. et al., (2009). MM3- ELISA Detection of Fasciola hepatica copro-antigens in preserved human stool samples.Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg., 81(1), pp.156-162. 72.Urs Duthaler, Laura Rinaldi, Maria P. Maurelli et al., (2010). Fasciola hepatica: Comparison of the sedimentation and FLOTAC techniques for the detection and quantification of faecal egg counts in rats. Experimental parasitology 126 (2010);161-166 73.Utzinger J, Chollet J, Tu Z, Xiao S, Tanner M, (2002). Comparative study of the effects of artemether and artesunate on juvenile and adult Schistosoma mansoni in experimentally infected mice. Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg 96:318-323. 74.Vicente Maco, Luis Marcos, Jaime Delgado et al., (2015). Efficacy and tolerability of two single-day regimens of triclabendazole for fascioliasis in Peruvian children. Rev Soc Bras Med Trop;48(4):445-53. 75.WHO (1998). Triclabendazole and fascioliasis - A new drug to combat an age-old disease, Fact sheet No 191. 76.WHO (2007). Report of the WHO Informal meeting on use of triclabendazole in fascioliasis control, WHO headquarters, Geneva, Switzerland. 77.WHO (2008). Foodborne disease outbreaks: Guidelines for investigation and control, pp.76. 78.WHO (2012). Foodborn trematode infection: Fascioliasis diagnosis, treatment and control strategy. Factsheet N°368. August 2012. 79.WHO/PAHO (2013). General information of fascioliasis - Neglected Tropical diseases. 80.WHO (2016). Foodborne trematodiases. Fact sheet, Updated in march 2016. 81.Winkelhagen AJS, Mank T, de Vries PJ, Soetekouw R. (2012). Apparent triclabendazole-resistant human Fasciola hepatica infection, the Netherlands. Emerg Infect Dis 2012;18:1028-9. 
Hình 9
82.Xuan L.T, Hung N.T, and Jitra W et al., (2005). Cutaneous fascioliasis: A case report in Vietnam”. Am J Trop Med Hyg, 72(5):508-509. 83.Yadav SC, Gupta SC (1988). on the viability of Fasciola gigantica metacercariae ingested by Lymnaea auricularia. J. Helminthol; 62:303-304. 84.Yakhchali, M., Imani Baran, A., Malekzadeh-Viayeh R. (2015). Molecular detection of the infection with Fasciola hepatica in field-collected snails of Galba truncatula and Lymnaea stagnalis from West Azarbaijan, Iran. Short Communication, Archives of Razi Institute, vol.70, No.3(2015):195-202 85.Yakoot M et al., (2010). A short review of the anthelminthic role of mirazid. Arq Gastroenterol. 47(4):393-394. 86.Yesildag A., Yildiz H., Demirci M., et al., (2009). Biliary fascioliasis: Sonographic appearance patterns. Journal of Clinical ultrasound, 37(1):26-30. 87.Yesildag A., Senol A., Koroglu M., Kockar C., et al., (2010). Hepatobiliary fascioliasis: A case with unusual radiological features. Diagn Interv Radiol, vol (16):299-301. 88.Yoshihara S, Ueno H. et al., (2004). Ingestion of Fasciola gigantica metacercariae by the intermediate host snail, Lymnaea ollula, and infectivity of discharged metacercariae. Southeast Asian J Trop Med Public Health;35:535-539. 89.Yvette M. Brockwell, Timothy P. Elliott, Glenn R. Anderson et al., (2014). Confirmation of Fasciola hepatica resistant to triclabendazole in naturally infected Australian beef and dairy cattle. International Journal for Parasitology: Drugs and drug resistance; 4(2014):48-54. 90.Zeynep Taş Cengiz, Hasan Yılmaz, Ahmet Cumhur Dülger et al., (2015). Seroprevalence of human fascioliasis in Van province, Turkey. Turk J Gastroenterol;26:259-62. 91.Marcos LA, Terashima A, Gotuzzo E. Update on hepatobiliary flukes: Fascioliasis, opisthorchiasis and clonorchiasis. Curr Opin Infect Dis. 2008;21:523–30. [PubMed] 92.Gonzalo-Orden M, Millán L, Alvarez M, Sánchez-Campos S, Jiménez R, González-Gallego J, et al. Diagnostic imaging in sheep hepatic fascioliasis: Ultrasound, computer tomography and magnetic resonance findings. Parasitol Res. 2003;90:359–64. [PubMed] 93.Mas-Coma S, Bargues MD, Valero MA. Fascioliasis and other plant-borne trematode zoonoses. Int J Parasitol. 2005;35:1255–78. [PubMed] 94.Lim JH, Mairiang E, Ahn GH. Biliary parasitic diseases including clonorchiasis, opisthorchiasis and fascioliasis. Abdom Imaging. 2008;33:157–65. [PubMed] 
Hình 10
95.Han JK, Jang HJ, Choi BI, Kim SH, Kim TK, Won HJ, et al. Experimental hepatobiliary fascioliasis in rabbits: A radiology-pathology correlation. Investig Radiol. 1999;34:99–108. [PubMed] 96.Cantisani V, Cantisani C, Mortelé K, Pagliara E, D’Onofrio M, Fernandez M, et al. Diagnostic imaging in the study of human hepatobiliary fascioliasis. Radiol Med. 2010;115:83–92. [PubMed] 97.Kabaalioglu A, Ceken K, Alimoglu E, Saba R, Cubuk M, Arslan G, et al. Hepatobiliary fascioliasis: sonographic and CT findings in 87 patients during the initial phase and long-term follow-up. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2007;189:824–8. [PubMed] 98.Koç Z, Ulusan S, Tokmak N. Hepatobiliary fascioliasis: Imaging characteristics with a new finding. Diagn Interv Radiol. 2009;15:247–51. [PubMed] 99.Alsaif HS, Venkatesh SK, Chan DS, Archuleta S. CT appearance of pyogenic liver abscesses caused by Klebsiella pneumoniae. Radiology. 2011;260:129–38. [PubMed] 100.Mortelé KJ, Segatto E, Ros PR. The infected liver: Radiologic-pathologic correlation. Radiographics. 2004;24:937–55. [PubMed]. 101.Dusak A, onur MR, Cicek M, Firat U, Ren T, Dogra VS. Radiological Imaging Features of Fasciola hepatica Infection - A Pictorial Review. J Clin Imaging Sci. 2012;2:2. doi: 10.4103/2156-7514.92372. Epub 2012 Jan 27. 102.Han JK, Jang HJ, Choi BI, Kim SH, Kim TK, Won HJ, Kim YI, Cho SY. Experimental hepatobiliary fascioliasis in rabbits: a radiology-pathology correlation. Invest Radiol. 1999 Feb;34(2):99-108. 103.Gonzalo-Orden M, Millán L, Alvarez M, Sánchez-Campos S, Jiménez R, González-Gallego J, Tuñón MJ. Diagnostic imaging in sheep hepatic fascioliasis: ultrasound, computer tomography and magnetic resonance findings. Parasitol Res. 2003 Aug;90(5):359-64. Epub 2003 Apr 17. 104.Kaya M, Beştaş R, Cetin S. Clinical presentation and management of Fasciola hepatica infection: single-center experience. World J Gastroenterol. 2011 Nov 28;17(44):4899-904. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v17.i44.4899. 
Hình 10
105.Lim JH, Mairiang E, Ahn GH. Biliary parasitic diseases including clonorchiasis, opisthorchiasis and fascioliasis. Abdom Imaging. 2008 Mar-Apr;33(2):157-65. Review. 106.Kiladze M, Chipashvili L, Abuladze D, Jatchvliani D. Obstruction of common bile duct caused by liver fluke--Fasciola hepatica. Sb Lek. 2000;101(3):255-9. 107.Menon P, Sinha AK, Rao KL, Khurana S, Lal S, Thapa BR. Biliary Fasciola gigantica infestation in a nonendemic area--An intraoperative surprise. J Pediatr Surg. 2015 Nov;50(11):1983-6. 108.Han JK, Choi BI, Cho JM, Chung KB, Han MC, Kim CW. Radiological findings of human fascioliasis. Abdom Imaging. 1993;18(3):261-4. 109.Christmann M, Henrich R, Mayer G, Ell C. Infection with fasciola hepatica causing elevated liver-enzyme results and eosinophilia - serologic and endoscopic diagnosis and therapy. Z Gastroenterol. 2002 Sep;40(9):801-6. German. 110.Onder H, Ekici F, Adin E, Kuday S, Gümüş H, Bilici A. An incidental case of biliary fascioliasis with subtle clinical findings: US and MRCP findings. Radiol oncol. 2013 May 21;47(2):125-7. doi: 10.2478/raon-2013-0021. 111.Aksoy DY, Kerimoglu U, Oto A, Erguven S, Arslan S, Unal S, Batman F, Bayraktar Y. Infection with Fasciola hepatica. Clin Microbiol Infect. 2005 Nov;11(11):859-61. 112.Ozturhan H, Emekdaş G, Sezgin O, Korkmaz M, Altintaş E. Seroepidemiology of Fasciola Hepatica in Mersin province and surrounding towns and the role of family history of the Fascioliasis in the transmission of the parasite. Turk J Gastroenterol. 2009 Sep;20(3):198-203. 
Hình 12
113.Gonzales Santana B, Dalton JP, Vasquez Camargo F, Parkinson M, Ndao M. The diagnosis of human fascioliasis by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) using recombinant cathepsin L protease. PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2013 Sep 19;7(9):e2414. doi: 10.1371/journal.pntd.0002414. eCollection 2013. 114.Valero MA, Perez-Crespo I, Periago MV, Khoubbane M, Mas-Coma S. Fluke egg characteristics for the diagnosis of human and animal fascioliasis by Fasciola hepatica and F. gigantica. Acta Trop. 2009 Aug;111(2):150-9. 115.Moazeni M, Ahmadi A. Controversial aspects of the life cycle of Fasciola hepatica. Exp Parasitol. 2016 Oct;169:81-9. doi: 10.1016/j.exppara.2016.07.010. Epub 2016 Jul 28. Review. 116.Karadağ-Öncel E, Ozsürekçi Y, Ozkaya-Parlakay A, Celik M, Cengiz AB, Haliloğlu M, Ceyhan M, Kara A. Fasciola hepatica infection: clinical and radiological findings in pediatric patients. Turk J Pediatr. 2012 Jul-Aug;54(4):362-7. 117.Mas-Coma S, Agramunt VH, Valero MA. Neurological and ocular fascioliasis in humans. Adv Parasitol. 2014;84:27-149. doi: 10.1016/B978-0-12-800099-1.00002-8. Review. 118.Sapmaz F, Kalkan IH, Guliter S, Nazlıoğlu A. A clinical presentation of a very rare infection: parenchymal Fasciola hepatica]. Turkiye Parazitol Derg. 2013;37(4):305-6. 119.Maeda T, Yamada H, Akao N, Iga M, Endo T, Koibuchi T, Nakamura T, Odawara T, Iwamoto A, Fujii T. Unusual radiological findings of Fasciola hepatica infection with huge cystic and multilocular lesions. Intern Med. 2008;47(5):449-52. Epub 2008 Mar 3. 120.Kim YH, Kang KJ, Kwon JH. Four cases of hepatic fascioliasis mimicking cholangiocarcinoma. Korean J Hepatol. 2005 Jun;11(2):169-75. Korean. 121.Behar JM, Winston JS, Borgstein R. Hepatic fascioliasis at a London hospital--the importance of recognising typical radiological features to avoid a delay in diagnosis. Br J Radiol. 2009 Aug;82(981):e189-93. doi: 10.1259/bjr/78759407. 122.Koç Z, Ulusan S, Tokmak N. Hepatobiliary fascioliasis: imaging characteristics with a new finding. Diagn Interv Radiol. 2009 Dec;15(4):247-51. doi: 10.4261/1305-3825.DIR.1851-08.2. Epub 2009 Nov 10. 123.Masake RA, Wescott RB, Spencer GR, Lang BZ. The pathogenesis of primary and secondary infection with Fasciola hepatica in mice. Vet Pathol. 1978 Nov;15(6):763-9. 124.Behzad C, Lahmi F, Iranshahi M, Mohammad Alizadeh AH. Finding of biliary fascioliasis by endoscopic ultrasonography in a patient with eosinophilic liver abscess. Case Rep Gastroenterol. 2014 Oct 8;8(2):310-8. doi: 10.1159/000367592. eCollection 2014 Sep. 125.Melero M, Rigou RC, Lloveras J, Gennaro O. Hepatic fascioliasis. Uncommon cause of prolonged febrile syndrome with hypereosinophilia and hypodense images on computed tomography of the liver. Medicina (B Aires). 1991;51(3):244-8. Spanish. 126.Patel NU, Bang TJ, Dodd GD 3rd. CT findings of human Fasciola hepatica infection: case reports and review of the literature. Clin Imaging. 2016 Mar-Apr;40(2):251-5. doi: 10.1016/j.clinimag.2015.11.002. Epub 2015 Nov 5. 127.Richter J, Freise S, Mull R, Millán JC. Fascioliasis: sonographic abnormalities of the biliary tract and evolution after treatment with triclabendazole. Trop Med Int Health. 1999 Nov;4(11):774-81. 128.Gajewska A, Smaga-Kozłowska K, Wiśniewski M. Pathological changes of liver in infection of Fasciola hepatica]. Wiad Parazytol. 2005;51(2):115-23. Review. Polish. 
Hình 13
 ' '
Hình 14
129.Chamadol N, Laopaiboon V, Techasatian P, Sukeepaisanjaroen W, Sripanuskul A. Computerized tomographic findings of hepatic fascioliasis compared with melioidosis-caused liver abscesses. J Med Assoc Thai. 2010 Jul;93(7):838-48. 130.Aksoy DY, Kerimoğlu U, Oto A, Ergüven S, Arslan S, Unal S, Batman F, Bayraktar Y. Fasciola hepatica infection: clinical and computerized tomographic findings of ten patients. Turk J Gastroenterol. 2006 Mar;17(1):40-5. 131.Kolodziejczyk L, Laszczyńska M, Masiuk M, Grabowska M, Skrzydlewska E. Immunoexpression of intermediate filaments and morphological changes in the liver and bile duct of rats infected with Fasciola hepatica. Biotech Histochem. 2015;90(7):477-85. doi: 10.3109/10520295.2015.1021712. Epub 2015 Apr 29. 132.Yilmaz B, Köklü S, Gedikoglu G. Hepatic mass caused by Fasciola hepatica: a tricky differential diagnosis. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 2013 Dec;89(6):1212-3. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.13-0085. Epub 2013 Sep 30. 133.Valero MA, Ubeira FM, Khoubbane M, Artigas P, Muiño L, Mezo M, Pérez-Crespo I, Periago MV, Mas-Coma S. MM3-ELISA evaluation of coproantigen release and serum antibody production in sheep experimentally infected with Fasciola hepatica and F. gigantica. Vet Parasitol. 2009 Jan 22;159(1):77-81. doi: 10.1016/j.vetpar.2008.10.014. Epub 2008 Oct 11. 134.Karahocagil MK, Akdeniz H, Sunnetcioglu M, Cicek M, Mete R, Akman N, Ceylan E, Karsen H, Yapici K. A familial outbreak of fascioliasis in Eastern Anatolia: a report with review of literature. Acta Trop. 2011 Jun;118(3):177-83. doi: 10.1016/j.actatropica.2008.08.013. 135.Millán JC, Mull R, Freise S, Richter J; Triclabendazole Study Group. The efficacy and tolerability of triclabendazole in Cuban patients with latent and chronic Fasciola hepatica infection. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 2000 Nov-Dec;63(5-6):264-9. 136.Chan FL, Chan JK, Leong LL. Modern imaging in the evaluation of hepatolithiasis. Hepatogastroenterology. 1997 Mar-Apr;44(14):358-69. Review. 137.Teke M, Önder H, Çiçek M, Hamidi C, Göya C, Çetinçakmak MG, Hattapoğlu S, Ülger BV. Sonographic findings of hepatobiliary fascioliasis accompanied by extrahepatic expansion and ectopic lesions. J Ultrasound Med. 2014 Dec;33(12):2105-11. doi: 10.7863/ultra.33.12.2105. 138.Jha AK, Goenka MK, Goenka U, Chakrabarti A. Hepatobiliary fascioliasis in non-endemic zones: a surprise diagnosis. Arab J Gastroenterol. 2013 Mar;14(1):29-30. doi: 10.1016/j.ajg.2012.12.005. Epub 2013 Jan 26. 139.Mohammad Alizadeh AH, Roshani M, Lahmi F, Davoodi NA, Rostami Nejad M, Seyyedmajidi MR, Zali MR. Cholangiocarcinoma in magnetic resonance cholangiopancreatography and fascioliasis in endoscopic ultrasonography. Case Rep Gastroenterol. 2011 Sep;5(3):569-77. doi: 10.1159/000333229. Epub 2011 Oct 1. 140.Ashrafi K, Bargues MD, O'Neill S, Mas-Coma S. Fascioliasis: a worldwide parasitic disease of importance in travel medicine. Travel Med Infect Dis. 2014 Nov-Dec;12(6 Pt A):636-49. doi: 10.1016/j.tmaid.2014.09.006. Epub 2014 Sep 28. Review. 141.Raadsma HW, Kingsford NM, Suharyanta, Spithill TW, Piedrafita D. Host responses during experimental infection with Fasciola gigantica or Fasciola hepatica in Merino sheep I. Comparative immunological and plasma biochemical changes during early infection. Vet Parasitol. 2007 Feb 28;143(3-4):275-86. Epub 2006 Oct 27. 142.Lee CW. The experimental studies on Capillaria hepatica] Kisaengchunghak Chapchi. 1964 Jun;2(1):63-80. Korean. 143.Yalav O, Yağmur Ö, Ülkü A, Akcam AT, Sönmez H. A rare cause of obstructive jaundice: Fasciola hepatica mimicking cholangiocarcinoma. Turk J Gastroenterol. 2012;23(5):604-7. 
Hình 15
144.Vaughan JL, Charles JA, Boray JC. Fasciola hepatica infection in farmed emus (Dromaius novaehollandiae). Aust Vet J. 1997 Nov;75(11):811-3. 145.Presidente PJ, McCraw BM, Lumsden JH. Experimentally induced Fasciola hepatica infection in white-tailed deer. II. Pathological features. Can J Comp Med. 1975 Apr;39(2):166-77. 146.Aroonroch R, Worawichawong S, Nitiyanant P, Kanchanapitak A, Bunyaratvej S. Hepatic fascioliasis due to Fasciola hepatica: a two-case report. J Med Assoc Thai. 2006 Oct;89(10):1770-4. 147.Kabaalioğlu A, Cubuk M, Senol U, Cevikol C, Karaali K, Apaydin A, Sindel T, Lüleci E. Fascioliasis: US, CT, and MRI findings with new observations. Abdom Imaging. 2000 Jul-Aug;25(4):400-4. 148.Timoteo O, Maco V Jr, Maco V, Neyra V, Yi PJ, Leguía G, Espinoza JR. Characterization of the humoral immune response in alpacas (Lama pacos) experimentally infected with Fasciola hepatica against cysteine proteinases Fas1 and Fas2 and histopathological findings. Vet Immunol Immunopathol. 2005 Jun 15;106(1-2):77-86. 149.Hanna RE, Cromie L, Taylor SM, Couper A. The effect of a parenteral ivermectin/closantel injection on the growth and reproductive development of early immature Fasciola hepatica in cattle. Vet Parasitol. 2006 Nov 30;142(1-2):78-90. Epub 2006 Aug 9. 150.Dracz RM, Lima Wdos S. Autochthonous infection of buffaloes and cattle by Fasciola hepatica in Minas Gerais, Brazil. Rev Bras Parasitol Vet. 2014 Jul-Sep;23(3):413-6. 151.Losada H, Hirsch M, Guzmán P, Fonseca F, Hofmann E, Alanís M. Fascioliasis simulating an intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma-Case report with imaging and pathology correlation. Hepatobiliary Surg Nutr. 2015 Feb;4(1):E1-7. doi: 10.3978/j.issn.2304-3881.2014.09.15. 152.Lim JH, Kim SY, Park CM. Parasitic diseases of the biliary tract. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2007 Jun;188(6):1596-603. Review. 153.Haseeb AN, el-Shazly AM, Arafa MA, Morsy AT. A review on fascioliasis in Egypt. J Egypt Soc Parasitol. 2002 Apr;32(1):317-54. Review. 154.Lee OJ, Kim TH. Indirect evidence of ectopic pancreatic fascioliasis in a human. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2006 Oct;21(10):1631-3. 
Hình 15
155.Ezzat RF, Karboli TA, Kasnazani KA, Hamawandi AM. Endoscopic management of biliary fascioliasis: a case report. J Med Case Rep. 2010 Mar 6;4:83. doi: 10.1186/1752-1947-4-83. 156.Han JK, Han D, Choi BI, Han MC. MR findings in human fascioliasis. Trop Med Int Health. 1996 Jun;1(3):367-72. 157.Graham CS, Brodie SB, Weller PF. Imported Fasciola hepatica infection in the United States and treatment with triclabendazole. Clin Infect Dis. 2001 Jul 1;33(1):1-5. Epub 2001 May 23. 158.Fullerton JK, Vitale M, Vitale GC. Therapeutic endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography for the treatment of Fasciola hepatica presenting as biliary obstruction. Surg Innov. 2006 Sep;13(3):179-82. 159.Escamilla A, Zafra R, Pérez J, McNeilly TN, Pacheco IL, Buffoni L, Martínez-Moreno FJ, Molina-Hernández V, Martínez-Moreno A. Distribution of Foxp3+ T cells in the liver and hepatic lymph nodes of goats and sheep experimentally infected with Fasciola hepatica. Vet Parasitol. 2016 Oct 30;230:14-19. doi: 10.1016/j.vetpar.2016.10.020. Epub 2016 Oct 23. 160.Beştaş R, Yalçin K, Çiçek M. Cholestasis caused by Fasciola gigantica. Turkiye Parazitol Derg. 2014;38(3):201-4. doi: 10.5152/tpd.2014.3212. 161.Pilet B, Deckers F, Pouillon M, Parizel P. Fasciola hepatica infection in a 65-year-old woman. J Radiol Case Rep. 2010;4(4):13-9. doi: 10.3941/jrcr.v4i4.384. Epub 2010 Apr 1. 162.Kaya M, Beştaş R, Gırgın S, Çıçek M, Kaplan MA. Increased anti-Echinococcus granulosus antibody positivity in Fasciola hepatica infection. Turk J Gastroenterol. 2012 Aug;23(4):339-43. 163.Rojas-Caraballo J, López-Abán J, Fernández-Soto P, Vicente B, Collía F, Muro A. Gene Expression Profile in the Liver of BALB/c Mice Infected with Fasciola hepatica. PLoS one. 2015 Aug 6;10(8):e0134910. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0134910. eCollection 2015. 
Hình 16
164.Foreyt WJ, Drew ML. Experimental infection of liver flukes, Fasciola hepatica and Fascioloides magna, in Bison (Bison bison). J Wildl Dis. 2010 Jan;46(1):283-6. 165.el-Newihi HM, Waked IA, Mihas AA. Biliary complications of Fasciola hepatica: the role of endoscopic retrograde cholangiography in management. J Clin Gastroenterol. 1995 Dec;21(4):309-11. 166.Carrada-Bravo T. Fascioliasis: diagnosis, epidemiology and treatment]. Rev Gastroenterol Mex. 2003 Apr-Jun;68(2):135-42. Review. Spanish. 167.Afshan K, Valero MA, Qayyum M, Peixoto RV, Magraner A, Mas-Coma S. Phenotypes of intermediate forms of Fasciola hepatica and F. gigantica in buffaloes from Central Punjab, Pakistan. J Helminthol. 2014 Dec;88(4):417-26. 168.Sampaio-Silva ML, Santoro F, Capron A. Circulating immune complexes in human fascioliasis. Relationship with Fasciola hepatica egg output. Acta Trop. 1981 Mar;38(1):39-44. 169.Sapunar J, Latorre R, Guerra M, Defilippi C. Clinical considerations on 2 cases of hepatic fascioliasis. Importance of the imaging examinations]. Bol Chil Parasitol. 1992 Jul-Dec;47(3-4):70-6. Spanish. 170.Castillo Contreras OB, Frisancho Velarde O. Hepatic pseudotumor in acute fascioliasis]. Acta Gastroenterol Latinoam. 2013 Mar;43(1):53-8. Spanish. 171.Colagrande S, Carmignani L, Pagliari A, Capaccioli L, Villari N. Transient hepatic attenuation differences (THAD) not connected to focal lesions. Radiol Med. 2002 Jul-Aug;104(1-2):25-43. English, Italian. 172.Rivero MA, Marcial MA. Biliary tract disease due to Fasciola hepatica: report of a case. Bol Asoc Med P R. 1989 Jul;81(7):272-4. 173.Carnevale S, Malandrini JB, Pantano ML, Sawicki M, Soria CC, Kuo LH, Kamenetzky L, Astudillo OG, Velásquez JN. Fasciola hepatica infection in humans: overcoming problems for the diagnosis. Acta Parasitol. 2016 Dec 1;61(4):776-783. doi: 10.1515/ap-2016-0107. 174.An integrated transcriptomics and proteomics analysis of the secretome of the helminth pathogen Fasciola hepatica: proteins associated with invasion and infection of the mammalian host. 175.Robinson MW, Menon R, Donnelly SM, Dalton JP, Ranganathan S. Mol Cell Proteomics. 2009 Aug;8(8):1891-907. doi: 10.1074/mcp.M900045-MCP200. Epub 2009 May 14. 176.Pfister K, Turner K, Currie A, Hall E, Jarrett EE. IgE production in rat fascioliasis. Parasite Immunol. 1983 Nov;5(6):587-93. 177.Stürchler D, Speiser F, Bogenmann F, Delmore G. Liver fascioliasis with unusual abscess formation. Case report]. Schweiz Med Wochenschr. 1981 Oct 17;111(42):1578-82. German. 178.Hillyer GV, Serrano AE. Fractionation of Fasciola hepatica tegument antigens and their application to the serodiagnosis of experimental fascioliasis by the enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. J Helminthol. 1986 Sep;60(3):173-8. 179.Inal M, Doran F, Soyupak S, Uğuz A, Akgül E, Okur N. Percutaneous biliary drainage: an alternative treatment for biliary fascioliasis. Abdom Imaging. 2002 Sep-Oct;27(5):552-6. 180.Roberts JA, Estuningsih E, Widjayanti S, Wiedosari E, Partoutomo S, Spithill TW. Resistance of Indonesian thin tail sheep against Fasciola gigantica and F. hepatica. Vet Parasitol. 1997 Jan;68(1-2):69-78. 181.Keshishian J, Brantley SG, Brady PG. Biliary fascioliasis mimicking sphincter of Oddi dysfunction. South Med J. 2010 Apr;103(4):366-8. doi: 10.1097/SMJ.0b013e3181d413d8. 182.Ashdhir P, Sharma SS, Sharma G. Biliary colic with dilated common bile duct: simple "sheepish" problem? J Indian Med Assoc. 2014 Feb;112(2):122-3. 183.Cosme A, Ojeda E, Cilla G, Torrado J, Alzate L, Beristain X, Orive V, Arenas J. Fasciola hepatica. study of a series of 37 patients. Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2001 Oct;24(8):375-80. Spanish. 184.Bechtel U, Feucht HE, Held E, Vogl T, Nothdurft HD. Fasciola hepatic infection in a family: diagnosis and therapy]. Dtsch Med Wochenschr. 1992 Jun 19;117(25):978-82. German. 185.Weiss D, Marti G, Mouton W, Wermke W, Kummer O. Infection with fasciola hepatica - a case series]. Ultraschall Med. 2010 Apr;31(2):175-81. doi: 10.1055/s-0029-1245188. Epub 2010 Feb 24. German. 186.Treacher RJ, Hughes DL, Harness E. The detection of liver cell damage by plasma enzyme changes in goats given immature Fasciola hepatica directly into the biliary system. Br Vet J. 1974 Jan-Feb;130(1):xii-xv. No abstract available. 187.Valero MA, Bargues MD, Khoubbane M, Artigas P, Quesada C, Berinde L, Ubeira FM, Mezo M, Hernandez JL, Agramunt VH, Mas-Coma S. Higher physiopathogenicity by Fasciola gigantica than by the genetically close F. hepatica: experimental long-term follow-up of biochemical markers. Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg. 2016 Jan;110(1):55-66. doi: 10.1093/trstmh/trv110. 188.Haseeb AN, el-Shazly AM, Arafa MA, Morsy AT. Evaluation of excretory/secretory Fasciola (Fhes) antigen in diagnosis of human fascioliasis. J Egypt Soc Parasitol. 2003 Apr;33(1):123-38. 189.Mas-Coma S, Valero MA, Bargues MD. Fasciola, lymnaeids and human fascioliasis, with a global overview on disease transmission, epidemiology, evolutionary genetics, molecular epidemiology and control. Adv Parasitol. 2009;69:41-146. doi: 10.1016/S0065-308X(09)69002-3. Review. 190.Ashrafi K, Valero MA, Peixoto RV, Artigas P, Panova M, Mas-Coma S. Distribution of Fasciola hepatica and F. gigantica in the endemic area of Guilan, Iran: Relationships between zonal overlap and phenotypic traits. Infect Genet Evol. 2015 Apr;31:95-109. doi: 10.1016/j.meegid.2015.01.009. Epub 2015 Jan 17. 191.Rajasekariah GR, Mitchell GF, Chapman CB, Montague PE. Fasciola hepatica: attempts to induce protection against infection in rats and mice by injection of excretory/secretory products of immature worms. Parasitology. 1979 Dec;79(3):393-400. 192.Ho AK, Girgis S, Low G. Uncommon liver lesions with multimodality imaging and pathology correlation. Clin Radiol. 2018 Feb;73(2):191-204. doi: 10.1016/j.crad.2017.07.016. Epub 2017 Sep 1. Review.
|

